Patient-specific implants are used in reconstructive cases where standard implants are not suitable. Design work is carried out in collaboration with the surgical team and based on the patient’s imaging and the planned reconstruction.
Virtual planning is used to review anatomy and material considerations in advance, allowing constraints and functional requirements to be addressed before manufacture.
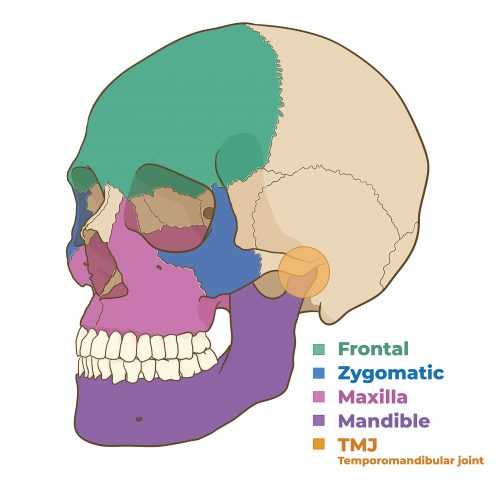
Prosthetic devices are manufactured according to typical stages:
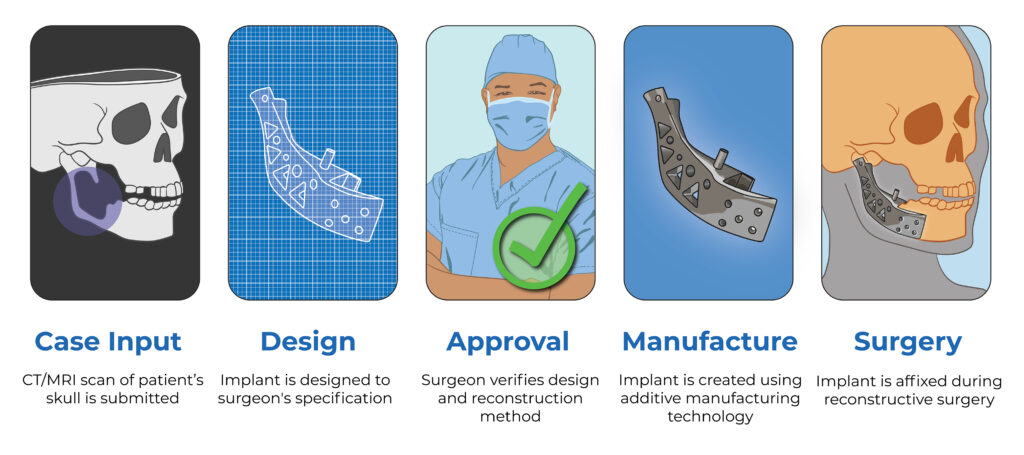
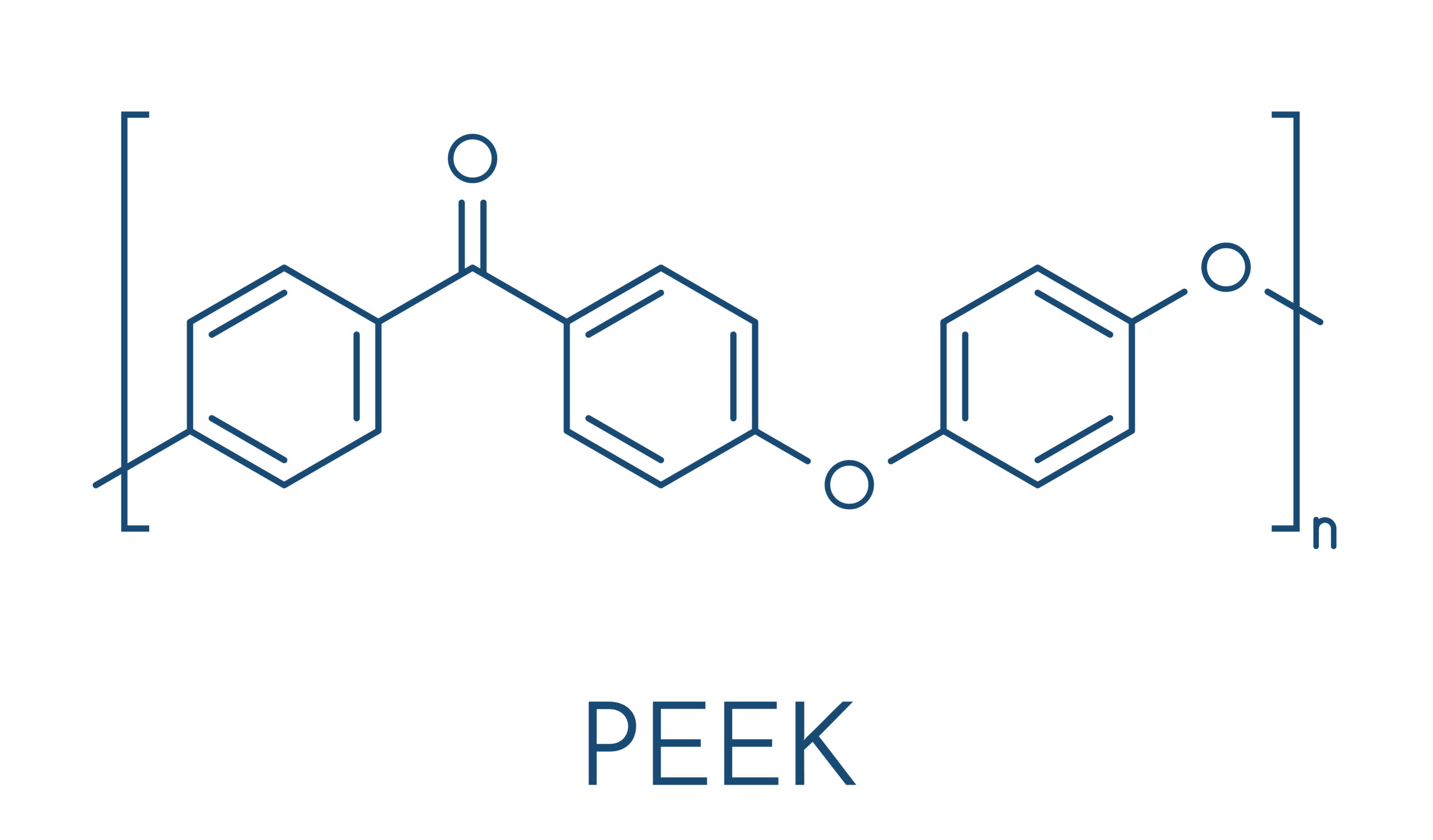
Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) and PEEK are commonly used for patient-specific implants, depending on the clinical requirements of the case. Material choice is guided by anatomy, fixation strategy, loading conditions, and surgeon preference.
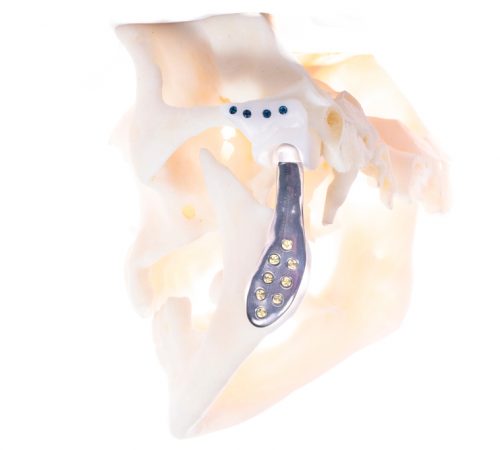
Titanium implants are widely used in cranio-maxillofacial reconstruction where strength, durability, and stable fixation are required. Titanium alloys are well established in clinical use and are compatible with bone contact and long-term implantation.
In practice, titanium is selected when rigid support, predictable mechanical behaviour, and compatibility with standard fixation methods are important. Its use in patient-specific implants allows geometry to be tailored to anatomy while maintaining familiar material behaviour in surgery.
PEEK is considered in patient-specific implant cases where a non-metallic material is preferred. This commonly includes situations where radiolucency is important for postoperative imaging, where metal artefact would interfere with assessment, or where the stiffness of a metal implant is not desirable for the surrounding anatomy.
In cranio-maxillofacial reconstruction, PEEK may be used when contour restoration is required without the need for rigid load-bearing support, or where proximity to sensitive structures makes metal implants less suitable. Material choice is discussed during planning and aligned with anatomical, functional, and imaging considerations rather than applied by default.
Selected case studies are available to illustrate typical clinical applications.
WhatsApp us